Asani Entertainment

“ASANI“
The male name Asani is pronounced – AA-SAA-NEE
ASANI’S LANGUAGE OF ORIGIN IS SWAHILI
THE NAME MEANS ‘REBELLIOUS’
For all of us life is death without adventure.
Adventure only comes to those who dare.
I am an Asanian and I’m inviting you to be one of us.

Adinkra are symbols from Ghana that represent concepts or aphorisms. Adinkra are used extensively in fabrics, logos and pottery. They are incorporated into walls and other architectural features. Adinkra symbols appear on some traditional Akan goldweights. The symbols are also carved on stools for domestic and ritual use. Tourism has led to new departures in the use of symbols in items such as T-shirts and jewelry.
The symbols have a decorative function but also represent objects that encapsulate evocative messages conveying traditional wisdom, aspects of life, or the environment. There are many symbols with distinct meanings, often linked with proverbs. In the words of Kwame Anthony Appiah, they were one of the means for “supporting the transmission of a complex and nuanced body of practice and belief”.
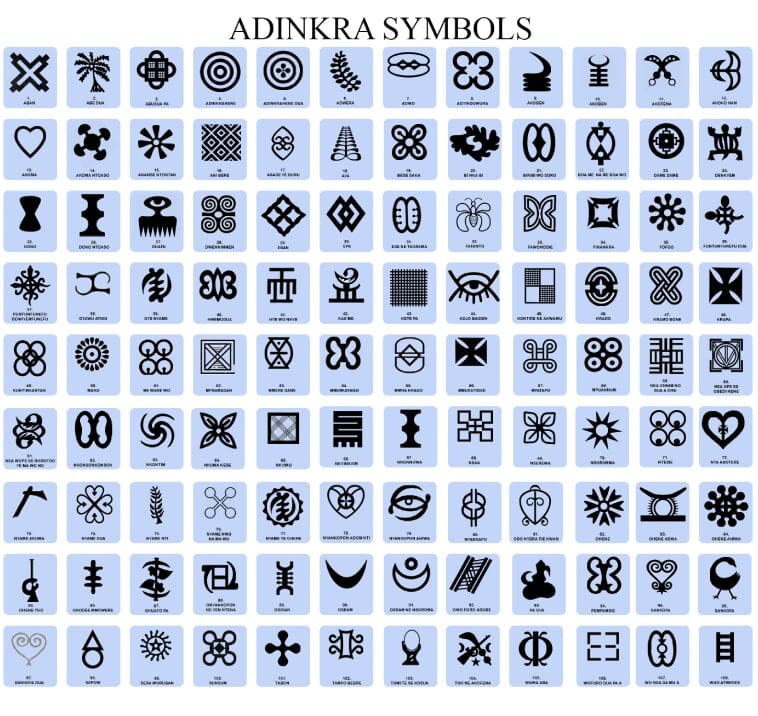
History
Adinkra symbols were originally created by the Bono people of Gyaman. The Gyaman king, Nana Kwadwo Agyemang Adinkra, originally created or designed these symbols, naming it after himself. The Adinkra symbols were largely used on pottery, stools etc. by the people of Bono. Adinkra cloth was worn by the king of Gyaman, and its usage spread from Bono Gyaman to Asante and other Akan kingdoms following its defeat. It is said that the guild designers who designed this cloth for the Kings were forced to teach the Asantes the craft. Gyaman king Nana Kwadwo Agyemang Adinkra’s first son, Apau, who was said to be well versed in the Adinkra craft, was forced to teach more about Adinkra cloths. Oral accounts have attested to the fact that Adinkra Apau taught the process to a man named Kwaku Dwaku in a town near Kumasi.
Over time, all Akan people including the Fante, Akuapem and Akyem all made Adinkra symbols a major part of their culture, as they all originated from the ancient Bono Kingdom. The oldest surviving adinkra cloth was made in 1817. The cloth features 15 stamped symbols, including nsroma (stars), dono ntoasuo (double Dono drums), and diamonds. The patterns were printed using carved calabash stamps and a vegetable-based dye. It has resided in the British Museum since 1818, when it was donated by Thomas E. Bowdich.
The next oldest piece of adinkra textile was sent in 1825 from the Elmina Castle to the royal cabinet of curiosities in The Hague, in response to an assignment from Major Friedrich Last, who was appointed temporary Commander of Dutch Gold Coast. He had the cloth commissioned from the Fante paramount chief of Elmina for William I of the Netherlands, which would explain why the coat of arms of the Netherlands is in the centre. The other motifs are typical of the older adinkras. It is now on display in the National Museum of Ethnology in Leiden.
In November 2020, a school board in York, Pennsylvania, banned “a children’s coloring book that featured African Adrinkra [sic] symbols found in fabrics, logos and pottery.” The decision was subsequently overturned.â€
Wikipedia
Welcome to The Evolution